Overeating? Mindfulness exercises may help
We all experience moments of indulgence that lead to overeating. If it happens once in a while, it’s nothing to worry about. If it happens frequently, you may wonder if you have an overeating problem or “food addiction.” Before you worry, know that neither of those is considered an official medical diagnosis. In fact, the existence of food addiction is hotly debated.
“If it exists, food addiction would be caused by an actual physiological process, and you’d experience withdrawal symptoms if you didn’t have certain foods, such as those with sugar. But that’s a lot different than saying you love sugar and it’s hard not to eat it,” notes Helen Burton Murray, a psychologist and director of the Gastrointestinal Behavioral Health Program in the Center for Neurointestinal Health at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Many people unconsciously overeat and don’t realize it until after they finish a meal. That’s where mindfulness exercises can help you stick to reasonable portion sizes.
But she urges you to seek professional help if your thoughts about eating are interfering with your ability to function each day. Your primary care doctor is a good place to start.
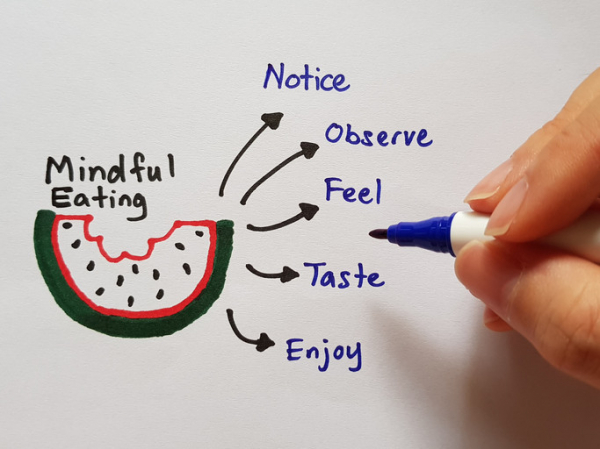
What is mindful eating?
Mindfulness is the practice of being present in the moment, and observing the inputs flooding your senses. At meal time: “Think about how the food looks, how it tastes and smells. What’s the texture? What memories does it bring up? How does it make you feel?” Burton Murray asks.
By being mindful at meals, you’ll slow the eating process, pay more attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, and perhaps avoid overeating.
“It makes you take a step back and make decisions about what you’re eating, rather than just going through the automatic process of see food, take food, eat food,” Burton Murray says.
Set yourself up for success in being mindful when you eat by:
- Removing distractions. Turn off phones, TVs, and computers. Eat in a peaceful, uncluttered space.
- Pacing yourself for a 20-minute meal. Chew your food slowly and put your fork down between bites.
More mindfulness exercises to try
Practicing mindfulness when you’re not eating sharpens your mindfulness “muscles.” Here are exercises to do that.
- Focused breathing. “Breathe in and breathe out slowly. With each in breath, allow your belly to go out. With each out breath, allow your belly to go in,” Burton Murray explains. “This engages the diaphragm, which is connected to the nerves between the brain and gut and promotes relaxation.”
- Progressive muscle relaxation. In this exercise, you tighten and release one major muscle group at a time for 20 seconds. As you release a contraction, notice how it feels for the muscles to relax.
- Take a mindful walk, even if it’s just for five minutes. “Use your senses to take in your surroundings,” Burton Murray suggests. “What colors are the leaves on trees? Are there cracks on the ground, and where are they? What does the air smell like? Do you feel a breeze on your skin?”
- Practice yoga or tai chi. Both of these ancient martial arts practices include deep breathing and a focus on body sensations.
- Keep a journal. Write down the details of your day. Try to include what your senses took in — the sights, sounds, and smells you experienced, and the textures you touched.
Don’t worry about trying to be mindful all day long. Start with a moment here and there and build gradually. The more mindful you become throughout your day, the more mindful you’ll become when you eat. And you may find that you’re better able to make decisions about the food you consume.
About the Author

Heidi Godman, Executive Editor, Harvard Health Letter
Heidi Godman is the executive editor of the Harvard Health Letter. Before coming to the Health Letter, she was an award-winning television news anchor and medical reporter for 25 years. Heidi was named a journalism fellow of the American Academy of Neurology, and has been honored by the Associated Press, the American Heart Association, the Wellness Community, and other organizations for outstanding medical reporting. Heidi holds a bachelor of science degree in journalism from West Virginia University. View all posts by Heidi Godman